
A fossil of an ape found in Turkey may debatably indicate that the ancestors of African apes and humans first evolved in Europe before migrating to Africa, a research team said in a new study.
This proposal bucks the traditional view that hominins—the group that includes humans, African apes (chimpanzees, bonobos, and gorillas) and their fossil ancestors—originated exclusively in Africa.
However, the discovery of many hominin fossils in Europe and Anatolia (modern Turkey) has already prompted some researchers To say that hominins first evolved in Europe. This view suggests that hominins later spread into Africa between 7 and 9 million years ago.
Study co-principal author David startedThe University of Toronto paleontologist explained that they are talking about the common ancestor of hominins, and not about the human lineage after it differed from the ancestors of humans. chimpanzee and bonobos, our closest living relatives.
“Since this divergence, most of human evolutionary history has occurred in Africa,” Begin told Live Science. “It is also likely that chimpanzee and human lineages diverged from each other in Africa.”
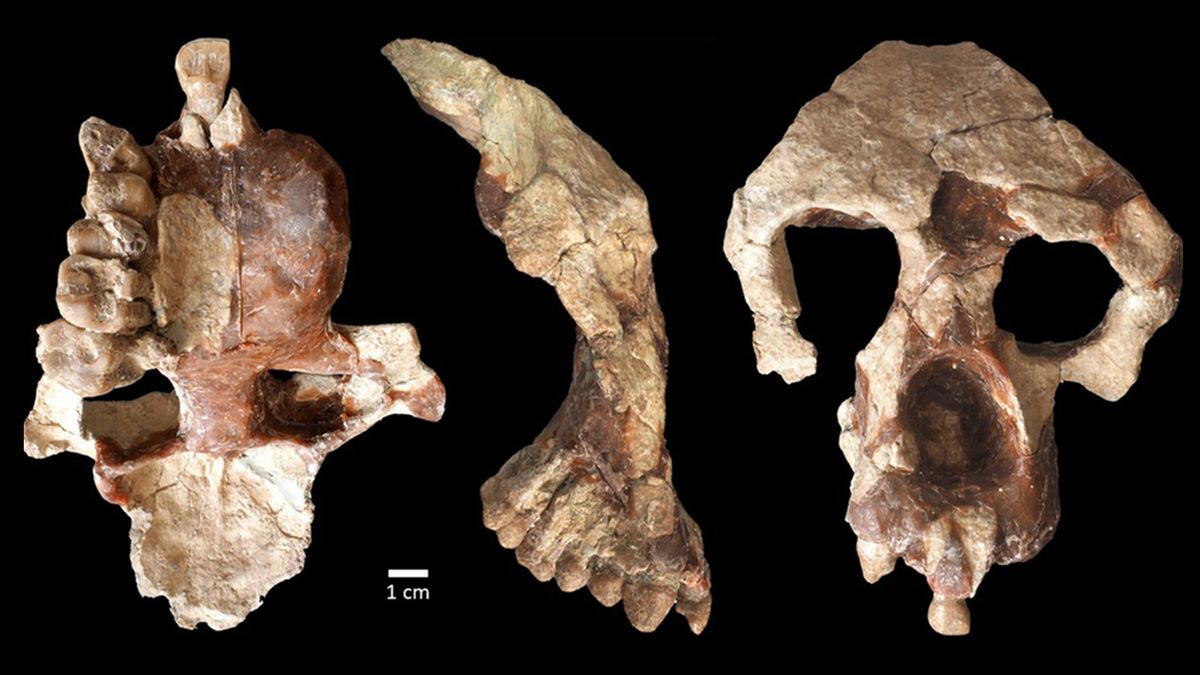
In the new study, the researchers analyzed a newly identified fossil of a monkey from the 8.7-million-year-old site of Korakierler in central Anatolia. They named it Species Turkish Anatolia. “Anatolia” is the modern Turkish word for Anatolia, and “Turk” refers to Turkey.
The fossil indicates that a. Turkish It likely weighed around 110 to 130 lb (50 to 60 kg), or about the weight of a large male chimpanzee.
Related: What was the last common ancestor of humans and apes like?
Based on the fossils of other animals found alongside it – such as giraffes, warthogs, rhinos, antelopes, zebras, elephants, porcupines and hyenas – as well as other geological evidence, the researchers suggest that the newly discovered ape lived in a dry forest. Like where the first humans might have lived in Africa, not in the forests of modern great apes. a. TurkishIts strong jaws and large teeth with thick enamel indicate that it may have eaten tough or tough foods such as roots, therefore a. Turkish He probably spent a great deal of time on Earth.
In the new study, scientists focused on a well-preserved partial skull discovered at the site in 2015. This fossil includes most of the structure of the face and the frontal part of the brain, the area where the brain sits, features that helped the team. Calculating evolutionary relationships.
“I was able to reconstruct and see the face of one of our ancestors for the first time that no one had seen before,” Begin said.
The researchers suggest that a. Turkish and other fossil apes from neighboring regions, eg Ouranopithecus In Greece and Turkey and Grecopithecus In Bulgaria, it formed a group of the first hominins. This, in turn, may indicate that the oldest hominins originated in Europe and the eastern Mediterranean. Specifically, the team asserts that ancient Balkan and Anatolian apes evolved from ancestors in Western and Central Europe.
Evolutionary questions

One question these findings raise is why, if hominins appeared in Europe, they are no longer present there, except for recently arrived humans, and why ancient hominins did not also spread into Asia, Begin said.
“The evolution is very unpredictable,” Begin said. “It occurs as a series of unconnected and random events that interact. We can assume that conditions were not suitable for movement into Asia from the eastern Mediterranean in the late Miocene, but they were suitable for spread into Africa.”
As for why “we don’t find African monkeys in Europe today, Species are becoming extinct “All the time,” Begin said.
Begin also cautioned that he did not want this research to be misinterpreted or misused to suggest that Eurasia was somehow fundamentally important to human evolution. Instead, he said, “We need to know where the common ancestor of African apes and humans evolved so that we can begin to understand the circumstances of that evolution.” “Between 14 million and 7 million years ago, the areas in which apes existed in Europe, Asia, and Africa were ecologically different, just as many areas on these continents are different today. Knowing the environmental conditions in which our ancestors evolved is crucial to understanding “Our origins.”
different look

This new discovery “expands our understanding of a group that appears closely related to living African apes and humans.” Christopher Gilberta paleontologist at Hunter College of the City University of New York who was not involved in this study, told Live Science.
However, Gilbert noted that recent comprehensive analyzes of fossils of great apes and early hominins — the group that includes humans and extinct species more closely related to humans than to any other animal — do not support the argument that hominins originated in Europe.
“Many other experts are investigating the evolutionary relationships between fossil and living great apes using more modern methods, including more [groups] “We found that many European apes diverged before orangutans, making them likely distant relatives of African great apes and humans,” Gilbert said.
Furthermore, these more comprehensive analyzes indicate that monkeys love Anatolovius “It is more likely or likely that they are new migrants to the Mediterranean from Africa rather than migrating back to Africa,” Gilbert added.
Fossil hominins like a. Turkish “They are not found in Africa largely because we have a generally poor African fossil record during this time,” Gilbert said. “I am reminded of the old axiom in paleontology – ‘absence of evidence is not evidence of absence’.”
However, Begin said the absence of hominin fossils in Africa was evidence and support for the idea that hominins had originated elsewhere.
However, Begin and Gilbert point out that future field work in Africa and Eurasia looking for fossil apes would help clarify this issue.
The scientists detail their findings August 23 in the journal Communications Biology.

“Typical beer advocate. Future teen idol. Unapologetic tv practitioner. Music trailblazer.”






More Stories
Boeing May Not Be Able to Operate Starliner Before Space Station Is Destroyed
How did black holes get so big and so fast? The answer lies in the darkness
UNC student to become youngest woman to cross space on Blue Origin